Leave Your Message
-
Whatsapp
-
Whatsapp
When choosing materials for construction, the decision between OSB board and plywood is crucial. Tom Richards, a renowned expert in the OSB Board Plywood industry, says, “Choosing the right material can define the success of your project.” As many builders navigate this choice, understanding the properties and applications of these materials becomes essential.
OSB board offers affordability and strength, making it popular for many projects. It is engineered wood, providing good insulation and moisture resistance. On the other hand, plywood is favored for its durability and versatility. Its layers give it unique strength and stunning finish options. However, the right choice often depends on specific project needs.
Both OSB board and plywood have their pros and cons. Builders lose time and resources when they make the wrong selection. Reflecting on your project's requirements is crucial. What might seem like a minor choice can have significant impacts down the line, especially in quality and longevity. Consider your goals carefully before deciding which direction to take.

OSB board and plywood are common choices in construction and woodworking. Each material has its unique properties and ideal applications. OSB is engineered from strands of wood. These strands are layered and bonded with adhesives. This makes OSB strong and durable. It is an excellent option for structural uses. A study by the APA – The Engineered Wood Association reports that OSB can perform similarly to plywood in many scenarios.
Plywood is composed of thin layers, or veneers, glued together. This layering grants plywood flexibility and resistance to warping. In many cases, plywood is favored for aesthetic applications. It is commonly used in furniture, cabinetry, and wall paneling. The Wood Products Council states that plywood often performs better in load-bearing situations.
Both materials have their pros and cons. OSB tends to be less expensive and is often used in flooring and roof sheathing. However, its appearance is often seen as less appealing. Plywood, while more costly, offers a more attractive surface. It's ideal for projects where visual appeal matters. In making your choice, consider the specific needs of your project.
| Property | OSB Board | Plywood |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Oriented strands of wood glued together | Thin layers of wood veneers glued together |
| Weight | Heavier than plywood | Lighter than OSB |
| Cost | Generally cheaper | More expensive |
| Moisture Resistance | Moderate, can swell when wet | Better moisture resistance |
| Strength | Strong and durable | Varies by grade but generally strong |
| Common Uses | Flooring, wall sheathing, roof decking | Furniture, cabinetry, high-end construction |
When comparing cost efficiency, OSB board and plywood present distinct financial attributes. According to recent industry studies, OSB typically costs 20-30% less than plywood. This difference stems from the manufacturing process. OSB is made from lower-grade wood fibers, making it cheaper to produce. However, this cost advantage comes with trade-offs in durability and moisture resistance.
Plywood, often praised for its strength, has a higher upfront cost. Yet, it can outperform OSB in moisture-prone environments. Long-term savings can occur with plywood due to its longevity. Industry reports indicate that plywood can last significantly longer than OSB, especially in exterior applications. While the initial price may be higher, this could mean fewer replacements over time.
Consider project needs carefully. If you're on a strict budget and the application isn't critical, OSB could suffice. If durability is paramount, plywood might be a better choice, despite the cost. Evaluating long-term use against immediate expenses is vital in making the right decision.
When selecting materials for construction, durability and strength are essential considerations. OSB (Oriented Strand Board) and plywood are widely used in various projects. OSB consists of wood strands bonded together in layers, making it a solid choice for many applications. In fact, structural tests reveal OSB can match or even surpass plywood in certain strength aspects.
A recent industry report indicates that OSB has improved significantly in moisture resistance over the years. It now performs well under wet conditions, an area where plywood typically excels. However, certain OSB types show a tendency to swell more than plywood in prolonged exposure to water. Users should tread cautiously here, as using OSB in high-moisture environments might not yield the best outcomes.
Plywood, on the other hand, is renowned for its versatility. Its layers are bonded with the grain alternating direction, giving it enhanced tensile strength. A substantial advantage is its resistance to splitting and warping. However, plywood may not be as cost-effective as OSB, especially for large projects. Cost differences can lead to tough decisions. Weighing the balance between price and longevity is crucial for anyone embarking on a construction journey.
When considering materials for construction projects, the environmental impact of OSB (Oriented Strand Board) and plywood proves to be crucial. Both materials have unique sustainability features. OSB, made from strands of wood, claims to use about 90% of the tree efficiently. According to a report from the Forest Products Laboratory, OSB production often results in less waste than plywood.
Plywood, however, typically requires more timber and involves a more energy-intensive process. The International Journal of Life Cycle Assessment has indicated that plywood may contribute to higher carbon emissions. Yet, it is also essential to recognize that not all plywood is sourced sustainably. The debate between these materials often hinges on sourcing practices. Certifications may not always guarantee a smaller carbon footprint.
Tips: When choosing materials, consider certifications, local sourcing, and production methods. Look for third-party verification to ensure sustainability claims.
OSB may be more renewable due to its manufacturing process, but it still has drawbacks. Depending on your project, the environmental costs of transportation and durability must be considered. Environmental factors change with location and use. A deeper understanding of both materials’ lifecycle is critical for a thoughtful decision.
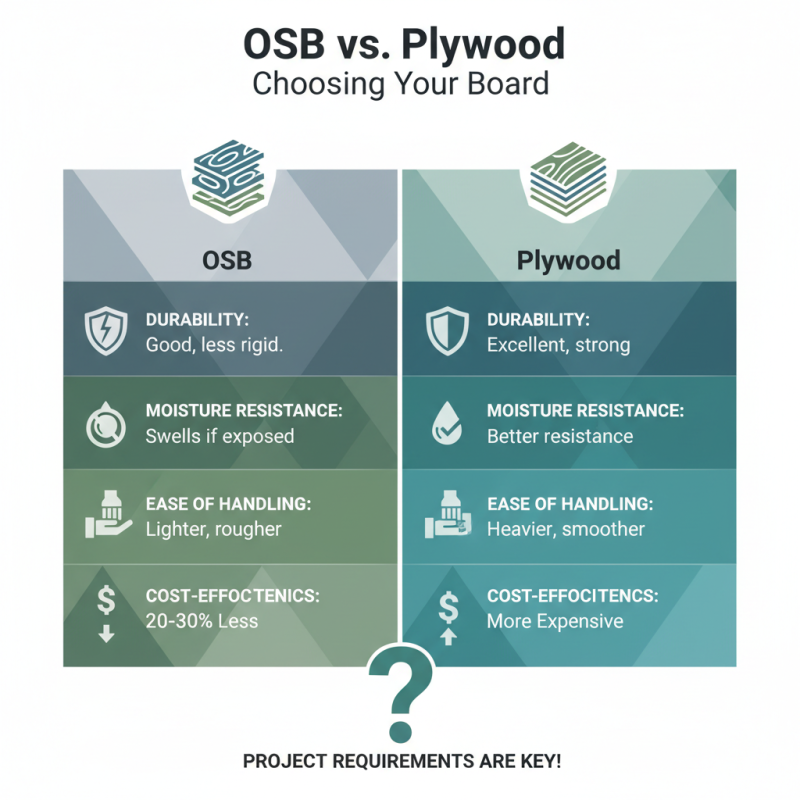
When it comes to choosing between OSB board and plywood, several factors play a crucial role. These factors include durability, moisture resistance, ease of handling, and cost-effectiveness. According to industry reports, OSB typically costs about 20-30% less than plywood. However, understanding the specific requirements of your project is essential.
Durability is key. OSB is engineered for strength and can handle heavy loads. On the other hand, plywood offers superior resistance to warping and shrinking. If your project involves exposure to moisture, plywood may be a better option due to its layered construction. Reports suggest that plywood performs better in humid conditions.
Tips: Consider the intended use of the material. For interior applications, OSB can be an economical choice. For exterior projects, opt for marine-grade plywood to withstand weather elements. Always factor in the availability of materials in your area. Limited access can increase costs unexpectedly.
When handling these materials, OSB can be bulkier and harder to maneuver. Plywood is lighter and easier to cut. Think about how you will handle these during your project. Sometimes, these details can lead to unexpected challenges. Don’t overlook the finishing process, as both materials require different treatment for optimal performance.