Leave Your Message
-
Whatsapp
-
Whatsapp
Blockboard Plywood is an intriguing material used in construction and furniture making. It consists of a core made from wooden blocks, which are sandwiched between two layers of plywood. This unique structure gives it strength and stability. Many artisans and builders prefer Blockboard Plywood for its affordability and versatility.
The material is often used for making doors, tables, and shelves. Its lightweight nature makes it easy to handle. However, it is crucial to consider its susceptibility to moisture. Proper sealing is necessary to prevent damage. Yet, even with precautions, some users have faced issues with durability over time.
Overall, Blockboard Plywood is a popular choice for many projects. Its benefits should be weighed against potential drawbacks. As with any material, thoughtful use is key. The more you understand it, the better your projects will turn out.
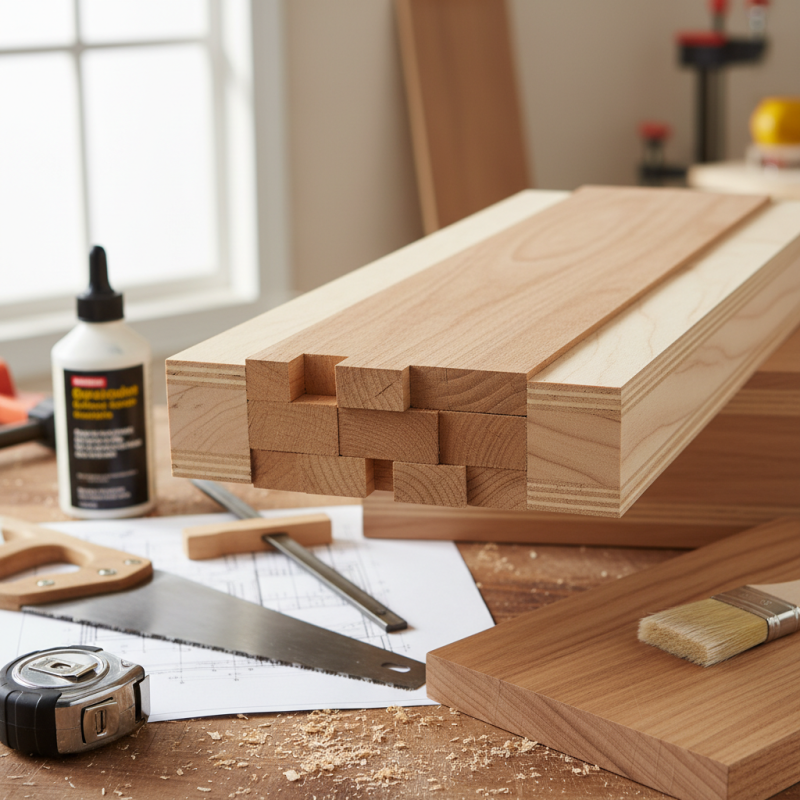

Blockboard plywood is a type of engineered wood. It consists of a core made from wooden strips, often softwood, sandwiched between layers of plywood. The strips are glued together at right angles, enhancing strength and stability. This structure minimizes warping, making it ideal for various applications.
In construction and furniture making, blockboard plywood serves multiple purposes. It is commonly used for doors, partitions, and tabletops. The surface is smooth and can be finished easily. However, potential drawbacks exist. Quality can vary based on the manufacturing process. Some blockboards may not withstand high moisture levels. Users must consider their specific needs and environments.
When selecting blockboard plywood, examining its composition is vital. Check for uniformity in the core. Look for smooth finishes, indicating better quality. Poorly made sheets may warp or bend. Understanding these factors can influence durability and usability. Reflecting on these aspects can improve your choices significantly.
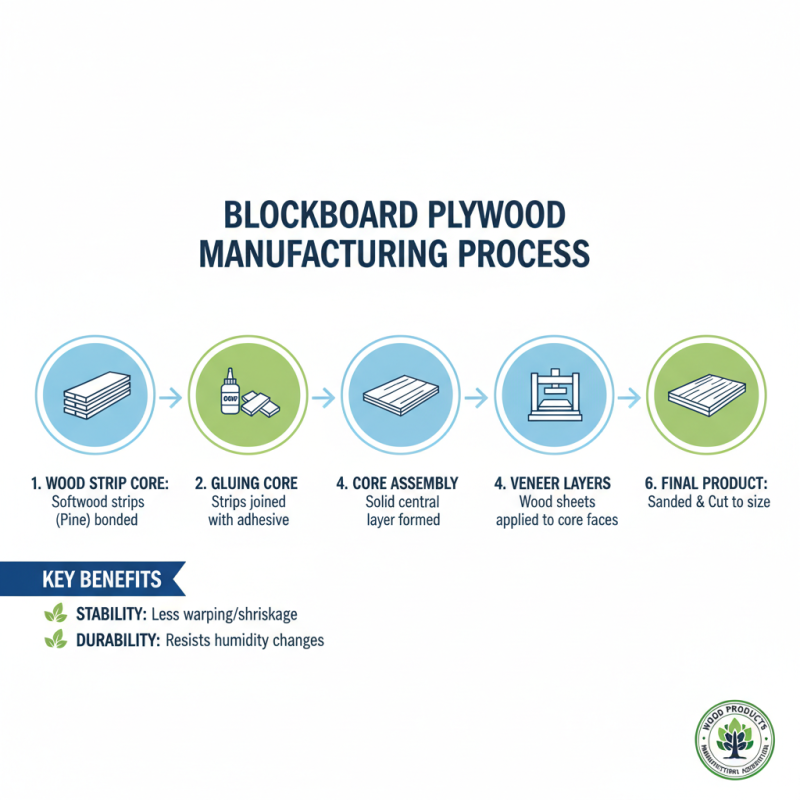
The manufacturing process of blockboard plywood involves several key steps. Initially, a core is created using strips of solid wood, typically softwoods like pine. These strips are glued together to form a strong central layer. This core structure provides stability and reduces warping compared to traditional plywood. A report from the Wood Products Manufacturers Association indicates that blockboard has a lower tendency to swell or shrink under varying humidity conditions.
After the core is assembled, it undergoes surface layering. Veneers, often made from hardwood, are glued to both sides. This adds aesthetic appeal and strength. Each layer is meticulously aligned to prevent defects. The assembly is then pressed under high pressure. A study by the Forest Products Laboratory highlights that this pressing technique ensures uniform adhesion and enhances durability.
Finishing touches involve sanding and surface treatment. Sanding smoothens the edges and ensures uniform thickness. Blockboard plywood can be easily cut and shaped for various applications, including furniture and cabinetry. However, challenges remain in uniform quality control across batches. Manufacturers strive for consistency, but variations can affect performance. Awareness of these issues is growing, prompting the industry to adopt more rigorous standards.
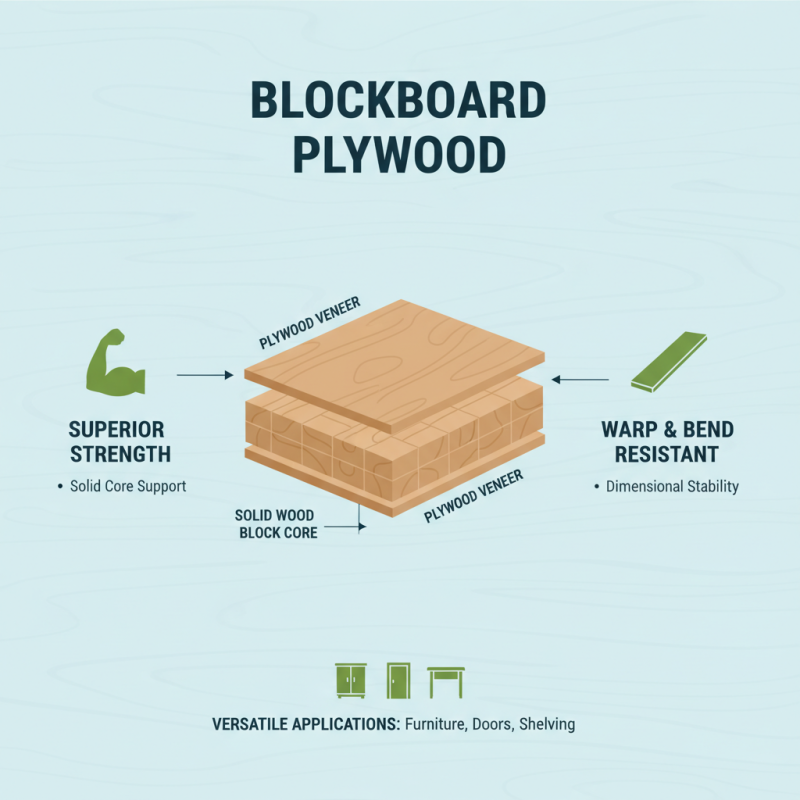
Blockboard plywood is an engineered wood product, widely appreciated for its unique properties. This material consists of a core made from solid blocks of wood, sandwiched between two layers of plywood. One of its main advantages is strength. The solid blocks provide excellent internal support. This structure helps it resist warping and bending, making it suitable for various applications.
Another notable feature of blockboard plywood is its lightweight nature. It is easier to handle compared to traditional solid wood. This characteristic allows for simple installation. Designers often choose it for furniture making, as it offers both durability and a smooth finish. The quality of its surface makes it ideal for painting and veneer applications, giving it an elegant look.
However, it's important to acknowledge certain limitations. Blockboard plywood may not withstand heavy moisture exposure, which could lead to damage. Users must consider this when choosing materials for specific environments. Additionally, its production process can vary, affecting overall quality. Careful selection is essential to ensure the best results in your projects.
Blockboard plywood is a versatile material used in many applications. One common use is in furniture production. Its lightweight quality allows for easy handling, making it ideal for items such as desks, cabinets, and shelves. Blockboard plywood often features a core made from softwood strips. This unique structure provides both durability and stability.
In building interiors, blockboard is a popular choice for doors. It can withstand pressure and resist warping, which is essential for high-traffic areas. According to industry reports, the demand for blockboard plywood in residential settings has increased by 10% in recent years. This growth indicates a trend towards sustainable and affordable building materials.
Additionally, blockboard plywood is utilized in the construction of partition walls. Its ability to be easily cut and shaped allows for creative designs. These partitions can define spaces without permanent alterations, fulfilling the needs of both homes and offices. However, sourcing quality materials is crucial. Not all blockboard plywood meets the industry standards, leading to potential issues. Making informed choices is vital for long-lasting applications.
Blockboard plywood requires regular maintenance to ensure longevity. Clean it often with a damp cloth to prevent dust buildup. Avoid using harsh chemicals that can damage its surface. A gentle cleaner is preferred. Sometimes, the edges may fray, which can be frustrating for users. Sanding them gently can fix this issue.
Humidity affects blockboard plywood significantly. Too much moisture can warp it. Keeping it in a dry area is essential. However, in dry conditions, it can crack. Finding a balance is difficult. Regular checks on humidity levels in the room help maintain its shape and integrity.
Occasional refinishing is beneficial. Apply a thin layer of polish or sealant. This not only enhances its appearance but also provides a protective layer. Yet, doing this too often might lead to build-up. Experiment to find the right timing. Notice how your blockboard plywood responds. Every piece is unique. Adjust your care routine accordingly.






